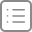
The scientific method uses a series of steps to establish facts or create knowledge. The overall process is well established, but the specifics of each step may change depending on what is being examined and who is performing it. The scientific method can only answer questions that can be proven or disproven through testing.
Make an observation or ask a question. The first step is to observe something that you would like to learn about or ask a question that you would like answered. These can be specific or general. Some cuamples would be “I observe that our total available network bandwidth drops at noon every weekday”or “How can we increase our website registration numbers?” Taking the time to establish a well-defined question will help you in later steps.
Gather background information.
This involves doing research into what is already known about the topic. This can also involve finding if anyone has already asked the same question.
Create a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is an explanation for the observation or question. If proven later, it can become a fact. Some examples would be “Our employees watching online videos during lunch is using our internet bandwidth”or “Our website visitors don’t see our registration form.”
Create a prediction and perform a test.
Create a testable prediction based on the hypothesis. The test should establish a noticeable change that can be measured or observed using empirical analysis. It is also important to control for other variables during the test. Some examples would be “If we block video-sharing sites , our available bandwidth will not go down significantly during lunch”or “If we make our registration box bigger, a greater percentage of visions will register for our website than before the change.”
Analyze the results and draw a conclusion.
Use the metrics established before the test see if the results match the production. For example, “After blocking video-sharing sites, our bandwidth utilization only went down by 10% frombefore; this is not enough of a change to be the primary cause of the network congestion”or “After increasing the size of the registration box, the percent of sign-ups went from 2% of totalpage views to 5%, showing that making the box larger results in more registrations.”
Share the conclusion or decide what question to ask next Document the results of your experiment.
By sharing the results with others, you also increase the total body of knowled ge available. Your experime nt may have also led to other questions, or if your hypothesis is disproven you may need to create a new one and test that. For example,“Because user activity is not the cause of excessive bandwidth use, we now suspect that an automated process is running at noon every day.”
What is the important role of collecting background information?
A. Make full preparation for the research questions.
B. Understand the knowledge of existing research results.
C. Provide evidence to refute the research conclusion.
D. Encourage researchers to reflect deeply on their work.答案:B In which case would it be necessary to create a new hypothesis for retesting?
A. The research hypothesis has been fully proved.
B. The research result s lead to other related issues.
C. The scope of test data needs to be expanded again.
D. The background investigation is not objective enough.答案:B What can we imfer from this passage?
A. Creating a question will help you in the following step.
B. Collecting information includes research on an unknown subject.
C. The test should establish a change that cannot be measured easily.
D. You may need to create a new hypothesis if the old one is overtained.答案:D